
On July 25, The International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO) announced its endorsement of the International Sustainability Standards Board’s (ISSB) Standards following its comprehensive review of the Standards.
IOSCO is now calling on its 130 member jurisdictions—capital markets authorities that regulate more than 95% of the world’s securities markets—to consider how they can incorporate the ISSB Standards into their respective regulatory frameworks to deliver consistency and comparability of sustainability-related disclosures worldwide.
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) achieved a momentous milestone on June 26th in advancing transparency and accountability in sustainability reporting. The release of its first-ever global sustainability disclosure standards create a standardized language for companies to communicate climate-related risks and opportunities, which the ISSB hopes will empower investors to make better-informed decisions. These new standards, known as IFRS S1 and IFRS S2, signal the beginning of a new era in sharing sustainability-related information across the world’s capital markets.
What is the ISSB?
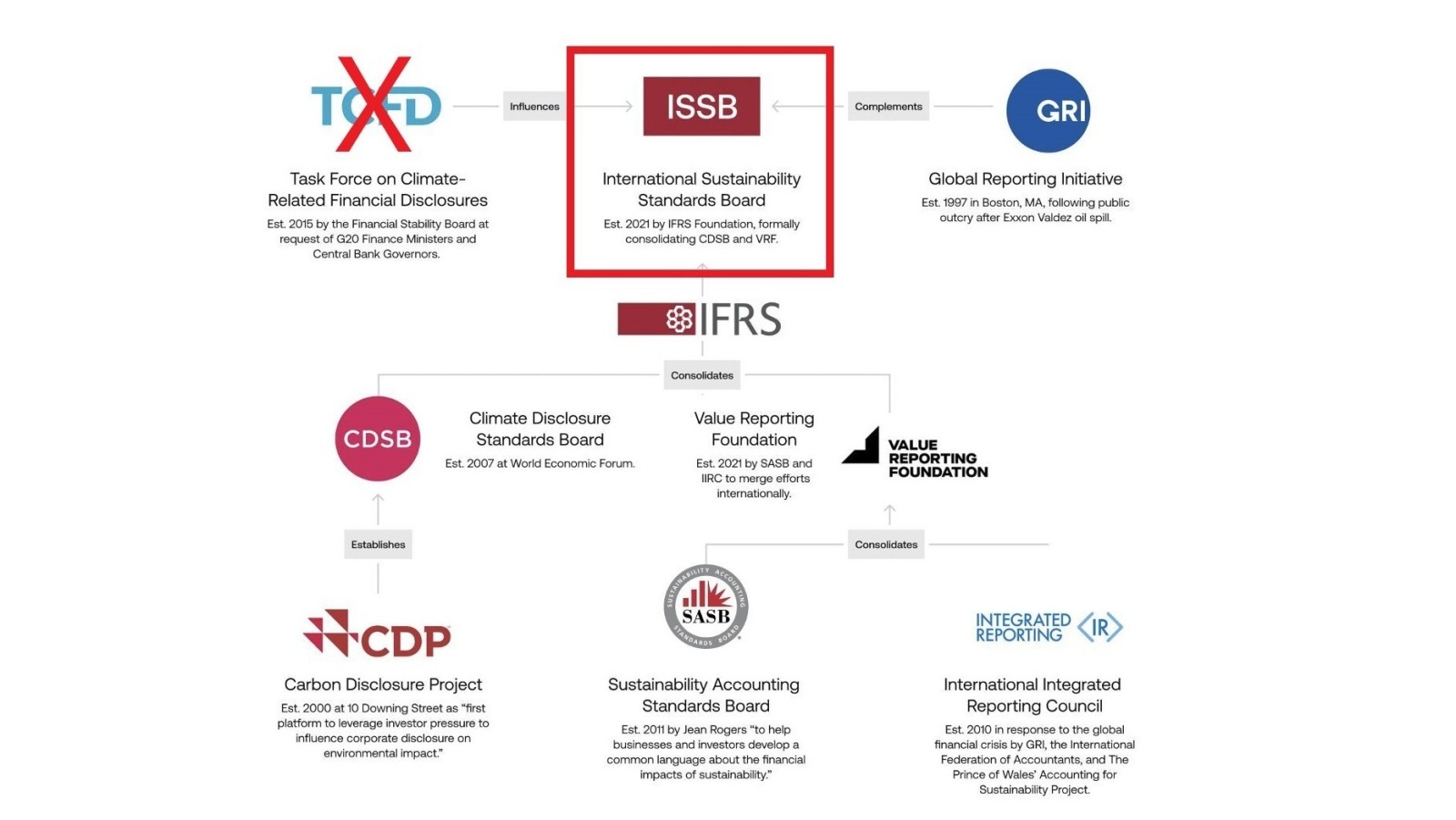
The ISSB was created by the IFRS Foundation in the fall of 2021 with a clear objective: to establish a comprehensive global framework of sustainability disclosure standards. Driven by the aim to fulfill the information requirements of investors and stakeholders, its formation was prompted by the widespread need in global capital markets for consistency, as multiple standards and frameworks were causing confusion.
What Are The IFRS S1 and IFRS S2 Standards?
IFRS S1 lays out rules for how companies should disclose financial information related to sustainability. These disclosures should be about the same company that provided the regular financial statements, and companies need to clarify which financial statements the sustainability information is connected to. The numbers and assumptions used in the sustainability information should match, as much as possible, the ones used in the regular financial statements, following the guidelines of IFRS Accounting Standards or other accepted accounting principles. Companies must also reveal any decisions they made and the sources they used while preparing this sustainability information. IFRS S1’s primary aim is to offer valuable insights to investors, facilitating a better understanding of how sustainability factors influence a company’s future potential.
Complementing IFRS S1, IFRS S2 is specifically focused on climate-related disclosures, ensuring a holistic approach to sustainability reporting. The IFRS S2 also has certain rules for disclosing specific measurements related to greenhouse gas emissions during a specific time period. These measurements include Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3 emissions. When disclosing these emissions following the guidelines of the Greenhouse Gas Protocol – A Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard (GHGP Standard) under IFRS S2, a company needs to mention the approach they used and the consolidated accounting group to which the emissions belong.
The ISSB Standards Timeline
The official launch of the ISSB Standards took place during the IFRS Foundation’s annual conference on June 26-27, 2023, with ISSB Chair Emmanuel Faber leading the event. These standards provide globally comparable information about sustainability-related risks and opportunities, a critical factor in investment decision-making.
The Standards are designed to be utilized by companies for their annual reporting periods starting on or after 1st January 2024. This means that the earliest these standards can be disclosed is in the companies’ 2025 annual reports. The required disclosures should be presented alongside the entity’s financial statements and cover the same reporting period.
For certain entities engaged in asset management, commercial banking, or insurance activities, there is an option for “transition relief” when applying the Standards. Entities that qualify for this relief are exempt from making specific disclosures during the initial annual reporting period when the Standards are implemented. This includes disclosures related to scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions and additional information about financed emissions, among others.
The New ISSB Standards Takes over TCFD
On July 10, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) asked the IFRS Foundation to take charge of monitoring companies’ progress in disclosing climate-related information. These ISSB Standards fully incorporate the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), which was set up in 2017 at the request of the Financial Stability Board.
In a statement from the IFRS Foundation confirming that it will take over the TCFD’s responsibilities, ISSB Chair Emmanuel Faber said: “The ISSB has built from and consolidated the market-leading investor-focused sustainability-reporting initiatives to deliver the ISSB Standards, with the TCFD recommendations at the heart of this. As such, the ISSB welcomes the FSB’s request to transfer the TCFD’s monitoring responsibilities to the ISSB from 2024 and the opportunity to build on TCFD’s legacy. This announcement provides yet further clarification of the so-called ‘alphabet soup’ of ESG initiatives for companies and investors.”
Starting in 2024, as the ISSB Standards will begin to apply globally, the IFRS Foundation will take over monitoring responsibilities from the TCFD, which was previously in charge of monitoring companies’ progress on climate-related disclosures based on their recommendations.



